Temple Tussle (Ranked)
Contents |
Temple Tussle Map Analysis
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Open terrain analysis: For each open terrain, count the number of adjacent open terrains. An open terrain has a minimum of 1 adjacent open terrain and a maximum of 8 open terrains. The quantity signifies the number of open terrains with X adjacent open terrains. The distribution indicates the map difficulty in relation to movement. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Offensive Map Control
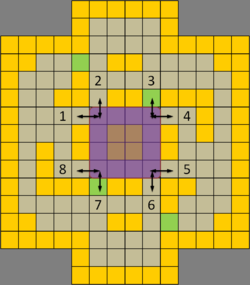
The Eight Paths
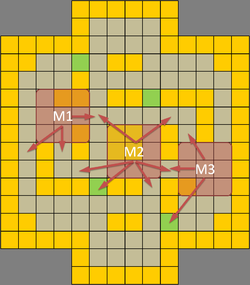
| Temple Tussle (TT) is a PVP map containing 224 terrains with 4 victory terrains. There are no impassable terrains and 4 difficult terrains. A central open 4x4 contest zone is surrounded on four sides by mini-mazes, creating a 'King of the Hill' (KotH) scenario. All figures adopt the 'offensive force attacking downwards and opponent defending upwards' orientation. As in usual KotH-like arenas, offensive control is established by winning areas leading into and out of the victory zone. As Figure 1 shows, there are 8 paths connected to the victory squares (highlighted in purple). Two paths involve difficult terrains, suited for ranged units. Whichever party successfully controls these pathways controls the game. However, it is impossible for a single party of 3 to simultaneously occupy 8 positions. Instead, we split the map into 3 distinctive zones and place units within those regions (Fig. 2) to cover as many paths as possible. By doing so, the map is set up for pincers and overlapping kill zones while allowing free flowing movement designed to punish isolated enemy units. Figure 3 show desirable positions that allow a team of melee units (attacking downwards) to exert map control on the opponent. M1 block enemies attempting to penetrate from the left lane while M3 block enemies from the right. M2 supports M1 and M3 by forming pincers and if need be, choke points to completely shut down enemy maneuvers into the lanes. Figure 4 show the same for a team of ranged units. Unlike melee units, ranged units set up overlapping kill zones to cover units attempting to penetrate the lanes and the victory terrains. Hence, the use of width and a higher strategic line of offense. Note that designations merely show preferable positions. In practice, hybrid teams work best to exert map control by covering each other with flexible positioning. | |||
Line of Sight
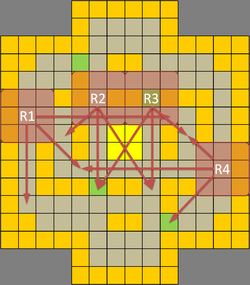
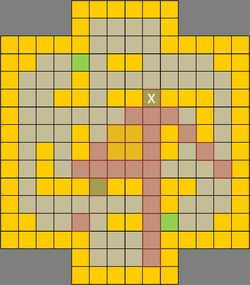
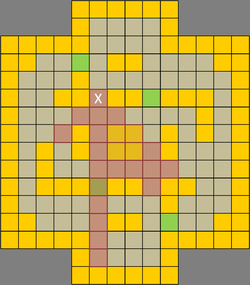
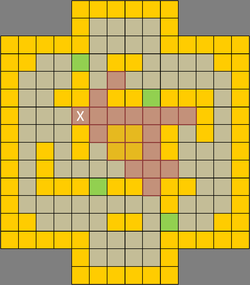
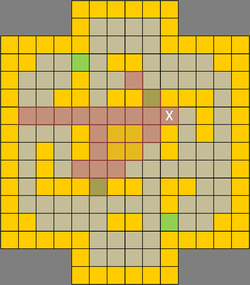
| Due to the many mazes and narrow lanes, line of sight (LoS) is a precious commodity crucial for ranged units in TT. The most valuable LoS are found in the eight lanes leading into the victory terrain (c.f. Figure 1 above). With map symmetry in mind, only four spots (paths 1, 2, 3 and 4) are discussed. Figures 5 to 8 below show the different areas of coverage. Of the various points, the LoS at path 3 (Fig. 5) denoted by X covers 25 squares which is the maximum compared to other lane spots. In addition, the underlying square has difficult terrain, making it a great sniper's spot and a perfect place to launch an offensive from. A ranged unit can simply back away when enemy melee units attempt to close in or lay down lava terrain to deter aggressors. A melee unit can choose to dominate the victory terrain or attempt to close down the right lane. Charging dwarves can pick any three lanes for rapid penetration. The sole drawback is a possible flanking move from the left lane and a single blindspot from the right. Figures 6 to 8 show the LoS of other paths. All provide sufficient coverage of the victory terrains and any two combinations are sufficient for creating overlapping kill zones. | |||
Defensive Map Control
Defensive Positioning
| Defensive map control is a risk averse approach to the game. It maximizes a party's effectiveness in combat through synergy and unit positioning, preventing flanking maneuvers and countering offensives. A basic tactic of defensive map control is defensive positioning utilizing available terrains, blind spots and ambush points to shut down the enemy. In TT, the easiest area to mount a defense from is right smack in the victory terrains. The four corners of the 4x4 central area cover all eight pathways and penalize any enemies attempting to breach. Allied units occupying victory terrains can choose to hunker down and blockade enemies through defensive positioning, focus attacks, stall tactics and frustration play. To pull off a successful blockade, mouse-over enemies' move cards and observe their possible movement ranges. Position units accordingly to shut down their mobility. Leave gaps between units for pincers. Figure 9 shows a defensive blockade for enemies attempting to breach from the right and bottom paths while figure 10 show the same for left and top paths. Over time, a defensive blockade can effectively shut down an enemy's gameplay options while gathering victory points. This forces your opponent to make rash decisions or foolish moves. The dark 'T' shaped area between the units show a pincer region. Enemies falling into this gap are flanked from all sides. Blocks and parries become inconsequential. |
Crowd Control
Crowd control (CC) is a term used in MMORPGs (Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games) and MOBA (Multiplayer Online Battle Arena) games to refer to the ability to limit the number of mobs actively fighting during an encounter. It also refers to abilities that influence or prevent the abilities or actions of other character(s). Crowd control is extremely powerful as it forces opponents to use a smaller set of abilities/actions, rendering an opponent nearly useless. In Card Hunter, CC is neither an offensive or defensive strategy. Instead it belongs in its own category and merits a separate discussion. In the context of a pvp map guide, we focus on terrain based forms of CC and present two useful examples centered around Wall of Stone and Wall of Illusion.
Wall of Stone (WoS)
Wall of Stone introduces up to three blocking terrains for a duration of two turns. TT is a great map for WoS. The narrow restrictive paths make it easy to shut down lanes, areas and cut off retreat routes. The most obvious being the area around the victory terrain. Figs. 11, 12 and 13 show zoomed-in illustrations of the various uses.